Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
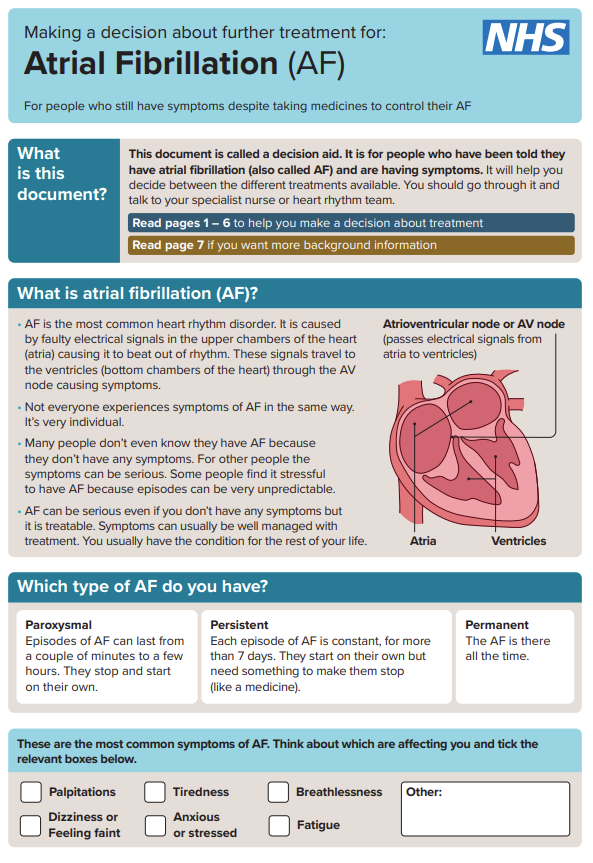
What is atrial fibrillation?
When the heart beats normally, its muscular walls contract (tighten and squeeze) to force blood out and around the body. They then relax, so the heart can fill with blood again. This process is repeated every time the heart beats.
What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
AF can cause problems including dizziness, shortness of breath and tiredness.
How can I check for atrial fibrillation?
A normal heart rate should be regular and between 60 and 100 beats per minute when resting.
Treating atrial fibrillation
Most people with AF will require an anticoagulant, but a small number of these won't as it depends on the risk.
Where else can I find helpful information?
- NHS Choices
- Care AF
- Diabetes UK
- British Heart Foundation
- Stroke Association
- Blood Pressure UK
- Arrhythmia Alliance
- Heart UK
Making a decision about further treatment for Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
This document is called a decision aid. It is for people who have been told they have atrial fibrillation (also called AF) and are having symptoms. It will help you decide between the different treatments available. You should go through it and talk to your specialist nurse or heart rhythm team.
NHS_Atrial_Fibrillation_decision_tool (england.nhs.uk)